| [1] Hu Y,Cai K,Luo Z,et al.Layer-by-layer assembly of b-estradiol loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles on titanium substrates and its implication for bone homeostasis.Adv Mater. 2010;22:4146-4150.
[2] Shi J,Votruba AR,Farokhzad OC,et al.Nanotechnology in drug delivery and tissue engineering: from discovery to applications. Nano Lett.2010;10(9):3223-3230.
[3] Lai M,Cai K,Zhao L,et al.Surface functionalization of TiO2 nanotubes with bone morphogenetic protein 2 and its synergistic effect on the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Biomacromolecules.2011;12(4):1097-1105.
[4] Hu Y,Cai K,Luo Z,et al.TiO2 nanotubes as drug nanoreservoirs for the regulation of mobility and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(1): 439-448.
[5] Tan AW,Pingguan-Murphy B,Ahmad R,et al.Review of titania nanotubes: Fabrication and cellular response.Ceramics International.2012;38(6):4421-4435.
[6] van Kooten C,Stax AS,Woltman AM,et al.Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology “Dendritic Cells”: the use of dexamethasone in the induction of tolerogenic DCs.Handb Exp Pharmacol.2009;(188):233-249.
[7] Baeuerle PA,Baichwal VR.NF-kappa B as a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory molecules.Adv Immunol.1997;65:111-137.
[8] Cameron K,Travers P,Chander C,et al.Directed osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem/precursor cells on silicate substituted calcium phosphate.Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A.2013;101(1):13-22.
[9] Fratoddi I,Venditti I,Cametti C,et al.Functional polymeric nanoparticles for dexamethasone loading and release.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;93:59-66.
[10] Su Y,Su Q,Liu W,et al.Controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and dexamethasone loaded in core–shell PLLACL–collagen fibers for use in bone tissue engineering.Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8(2):763-771.
[11] Yu WQ,Zhang YL,Jiang XQ,et al.In vitro behavior of MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast with different annealing temperature titania nanotubes.Oral Dis.2010;16 (7):624-630.
[12] Hu X,Shen H,Shuai K,et al.Surface bioactivity modification of titanium by CO2 plasma treatment and induction of hydroxyapatite: in vitro and in vivo studies. Appl Surf Sci. 2011; 257(6):1813-1823.
[13] Bajgai MP,Parajuli DC,Park SJ,et al.In vitro bioactivity of sol-gel-derived hydroxyapatite particulate nanofiber modified titanium.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(2):685-694.
[14] Bai Y,Park IS,Park HH,et al.The effect of annealing temperatures on surface properties, hydroxyapatite growth and cell behaviors of TiO2 nanotubes. Surf Interf Analysis. 2011;43(6):998-1005.
[15] Yu WQ,Jiang XQ,Zhang FQ,et al.The effect of anatase TiO2 nanotube layers on MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010; 94(4):1012-1022.
[16] Wang CY,Zhao BH,Ai HJ,et al.Comparison of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells grown on two different titanium implant surfaces.Biomed Mater. 2008;3(1): 015004.
[17] Mellado-Valero A,Buitrago-Vera P,Solá-Ruiz MF,et al.Decontamination of dental implant surface in peri-implantitis treatment: A literature review.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal.2013;18(6):e869-e876.
[18] Wennerberg A,Albrektsson T,Johansson C,et al.Experimental study of turned and grit-blasted screw-shaped implants with special emphasis on effects of blasting material and surface topography.Biomaterials.1996;17(1):15-22.
[19] Kim HW,Koh YH,Li LH,et al.Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate with titania buffer layer processed by solgel method.Biomaterials.2004;25 (13):2533-2538.
[20] Mamalis A,Silvestros S.Modified titanium surfaces alter osteogenic differentiation: a comparative microarray-based analysis of human mesenchymal cell response to commercial titanium surfaces.J Oral Implantol. 2013;39(5):591-601.
[21] Kim MJ,Kim CW,Lim YJ,et al.Microrough titanium surface affects biologic response in MG63 osteoblast‐like cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(4):1023-1032.
[22] Saito T,Hayashi H,Kameyama T,et al.Suppressed proliferation of mouse osteoblast-like cells by a rough-surfaced substrate leads to low differentiation and mineralization.Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30(1):1-7.
[23] Schwartz Z,Olivares-Navarrete R,Wieland M,et al. Mechanisms regulating increased production of osteoprotegerin by osteoblasts cultured on microstructured titanium surfaces.Biomaterials.2009;30(20):3390-3396.
[24] Liu H,Webster TJ.Nanomedicine for implants: A review of studies and necessary experimental tools. Biomaterials. 2007;28(2):354-369.
[25] Chen ZX,Takao Y,Wang WX,et al.Surface characteristics and in vitro biocompatibility of titanium anodized in a phosphoric acid solution at different voltages.Biomed. Mater.2009;4(6):
[26] Yu WQ,Qiu J,Zhang FQ.In vitro corrosion study of different TiO2 nanotube layers on titanium in solution with serum proteins.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2011;84(2):400-405.
[27] Swami N,Cui Z,Nair LS.Titania Nanotubes, Novel nanostructures for improved osseointegration.J Heat Transfer. 2011;133(3):034002.
[28] Kim HM,Chae WP,Chang KW,et al.Composite nanofiber mats consisting of hydroxyapatite and titania for biomedical applications.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;94(2): 380-387.
[29] Simchi A,Tamjid E,Pishbin F,et al.Recent progress in inorganic and composite coatings with bactericidal capability for orthopaedic applications. Nanomedicine.2011;7(1):22-39.
[30] Gao L,Feng B,Wang J,et al.Micro/nanostructural porous surface on titanium and bioactivity.J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater.2009;89(2):335-341.
[31] Zhao L,Mei S,Chu PK,et al.The influence of hierarchical hybrid micro/nano-textured titanium surface with titania nanotubes on osteoblast functions. Biomaterials. 2010;31(19): 5072-5082.
[32] Sato M,Sambito MA,Aslani A,et al.Increased osteoblast functions on undoped and yttrium-doped nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium.Biomaterials. 2006;27(11): 2358-2369.
[33] Popat KC,Leoni L,Grimes CA,et al.Influence of engineered titania nanotubular surfaces on bone cells.Biomaterials. 2007; 28(21):3188-3197.
[34] Oh S,Brammer KS,Li Y S J,et al.Stem cell fate dictated solely by altered nanotube dimension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(7):2130-2135.
[35] Minagar S,Berndt CC,Wang J,et al.A review of the application of anodization for the fabrication of nanotubes on metal implant surfaces.Acta biomaterialia. 2012;8(8):2875-2888.
[36] Karla S,Seunghan O.Improved bone-forming functionality on diameter-controlled TiO2 nanotube surface.Acta Biomaterialia. 2009;5(8):3215-3223.
[37] Discher DE,Mooney DJ,Zandstra PW. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells.Science. 2009;324(5935):1673-1677.
[38] Kang Y,Kim S,Khademhosseini A,et al.Creation of bony microenvironment with CaP and cell-derived ECM to enhance human bone-marrow MSC behavior and delivery of BMP-2. Biomaterials.2011;32(26):6119-6130.
[39] Macdonald ML,Samuel RE,Shah NJ,et al.Tissue integration of growth factor-eluting layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte multilayer coated implants. Biomaterials. 2011;32(5): 1446-1453.
[40] Balaur E,Macak JM,Tsuchiya H,et al.Wetting behaviour of layers of TiO2 nanotubes with different diameters.J Mater Chem.2005;15:4488-4491.
[41] Hu Y,Cai K,Luo Z,et al.Regulation of the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and osteogenesis in vivo by microenvironmental modification of titanium alloy surfaces. Biomaterials.2012;33(13):3515-3528.
[42] 关林波,但卫华,曾睿,等.明胶及其在生物材料中的应用[J].材料导报,2006,20(S2):380-383.
[43] 罗华丽,鲁在君.壳聚糖作为药物缓释载体的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2006,19(7):25-30.
[44] Son JS,Choi YA,Park EK,et al.Drug delivery from hydroxyapatite-coated titanium surfaces using biodegradable particle carriers.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013; 101(2):247-257.
[45] Cai KY,Hu Y,Luo Z,et al.Cell-speci?c gene transfection from a gene-functionalized poly(D,L-lactic acid) substrate fabricated by the layer-by-layer assembly technique.Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008’47;(39):7479-7481. |
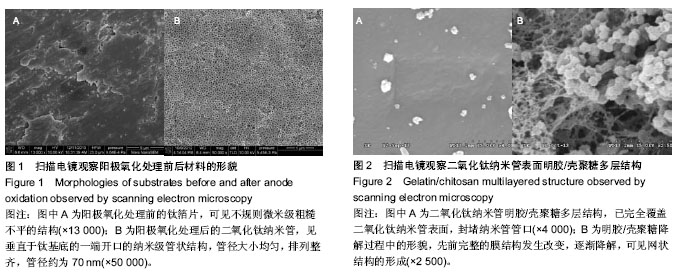
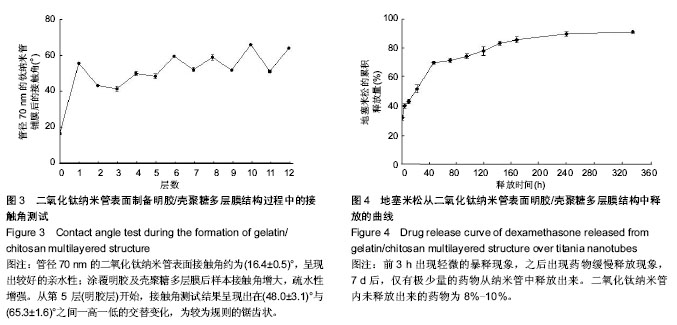
.jpg)
